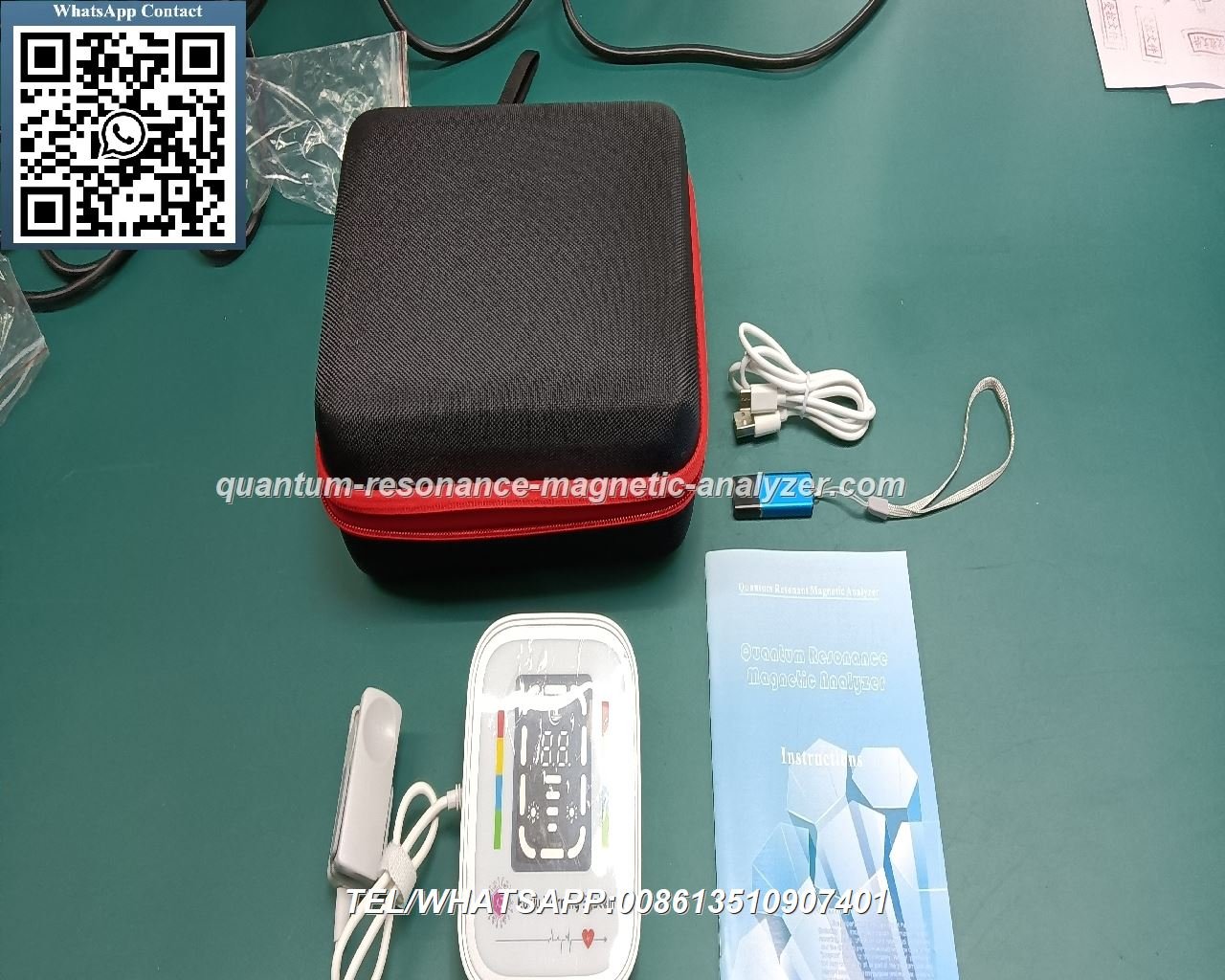
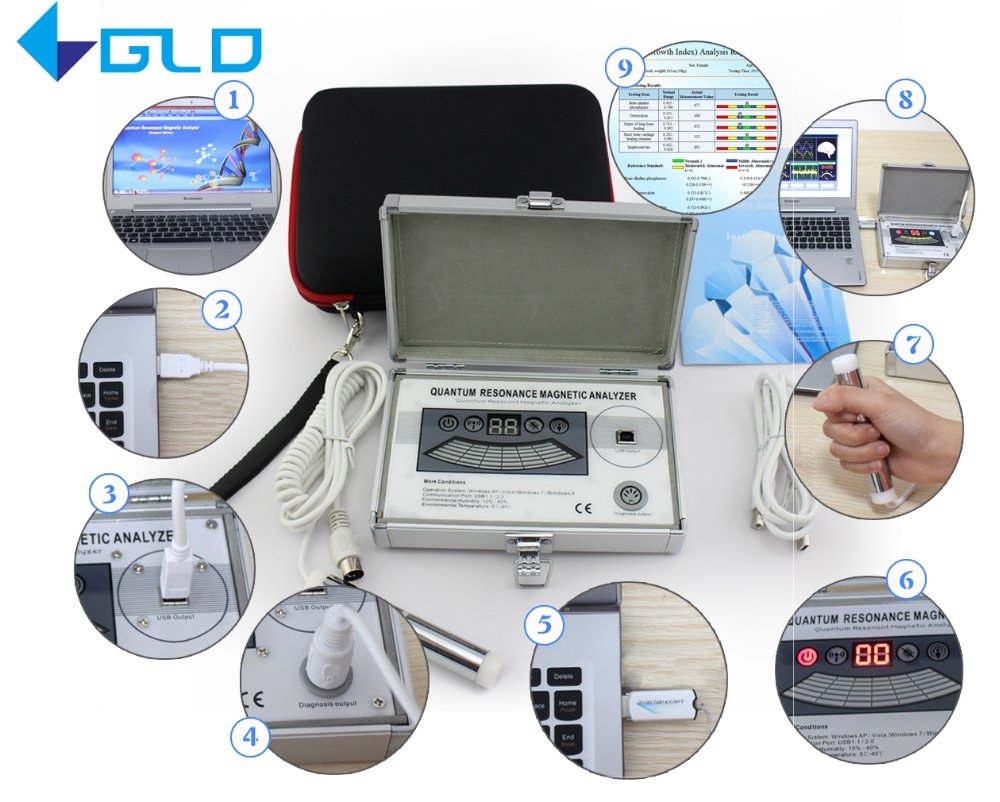
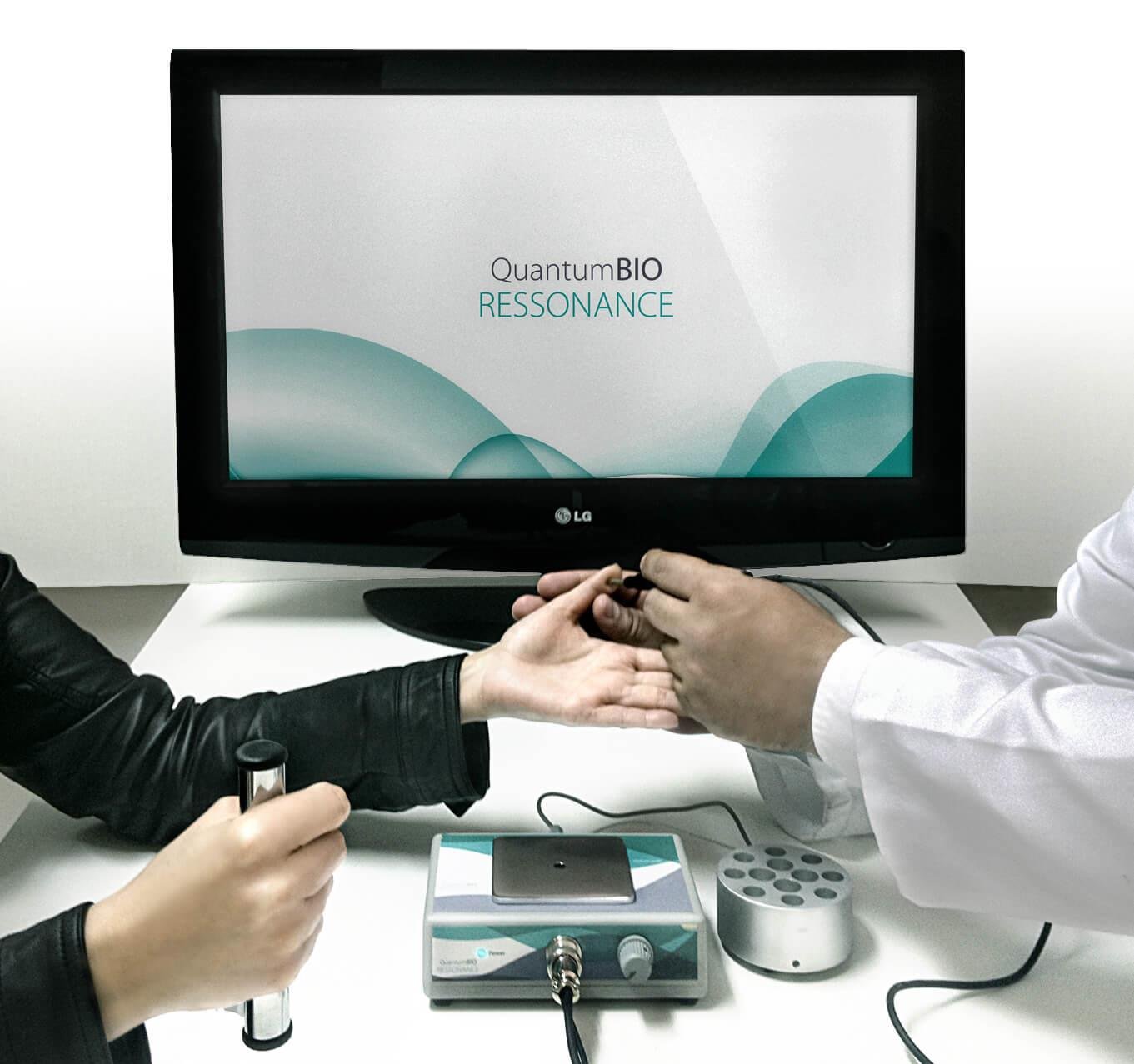
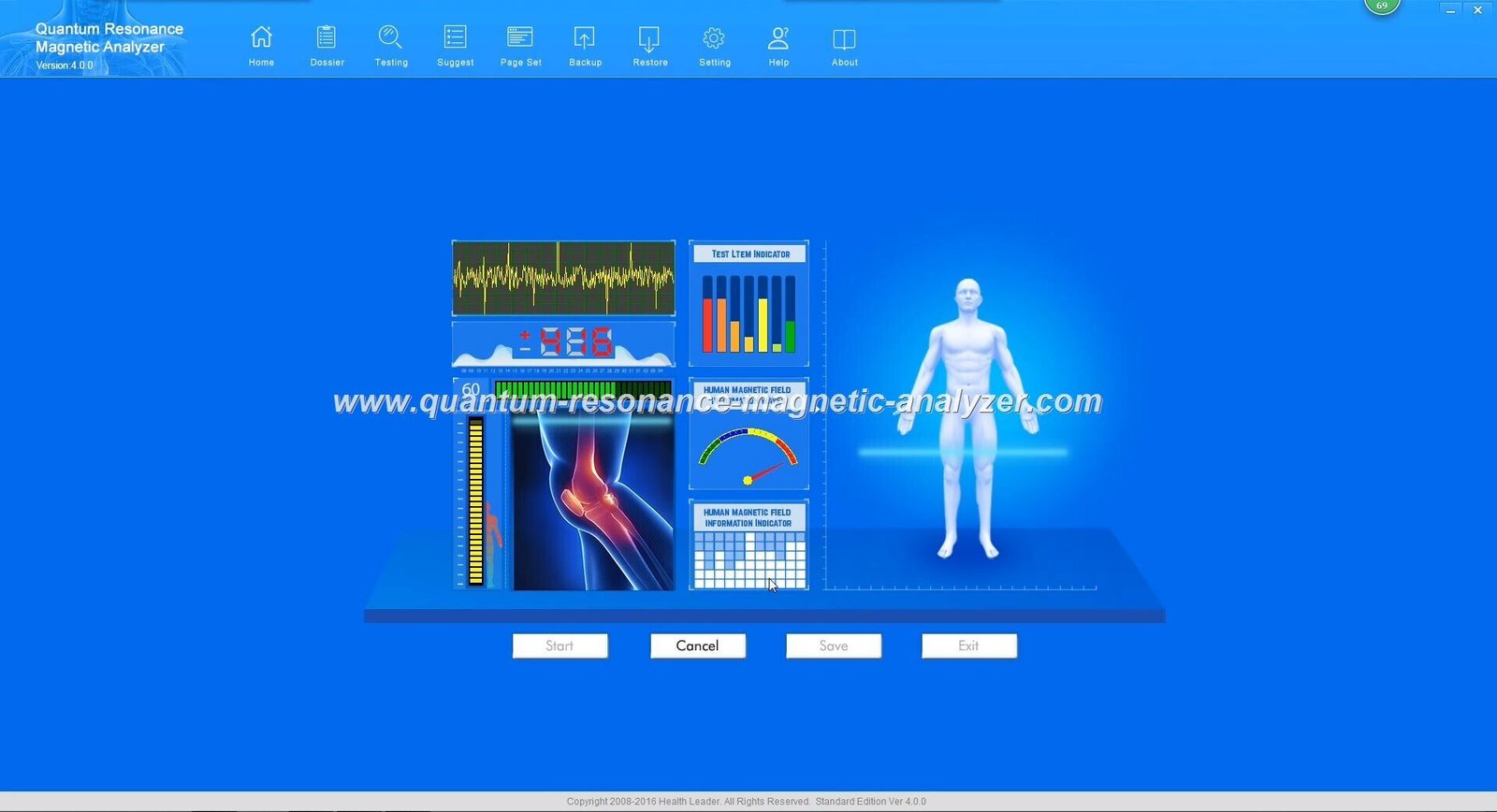
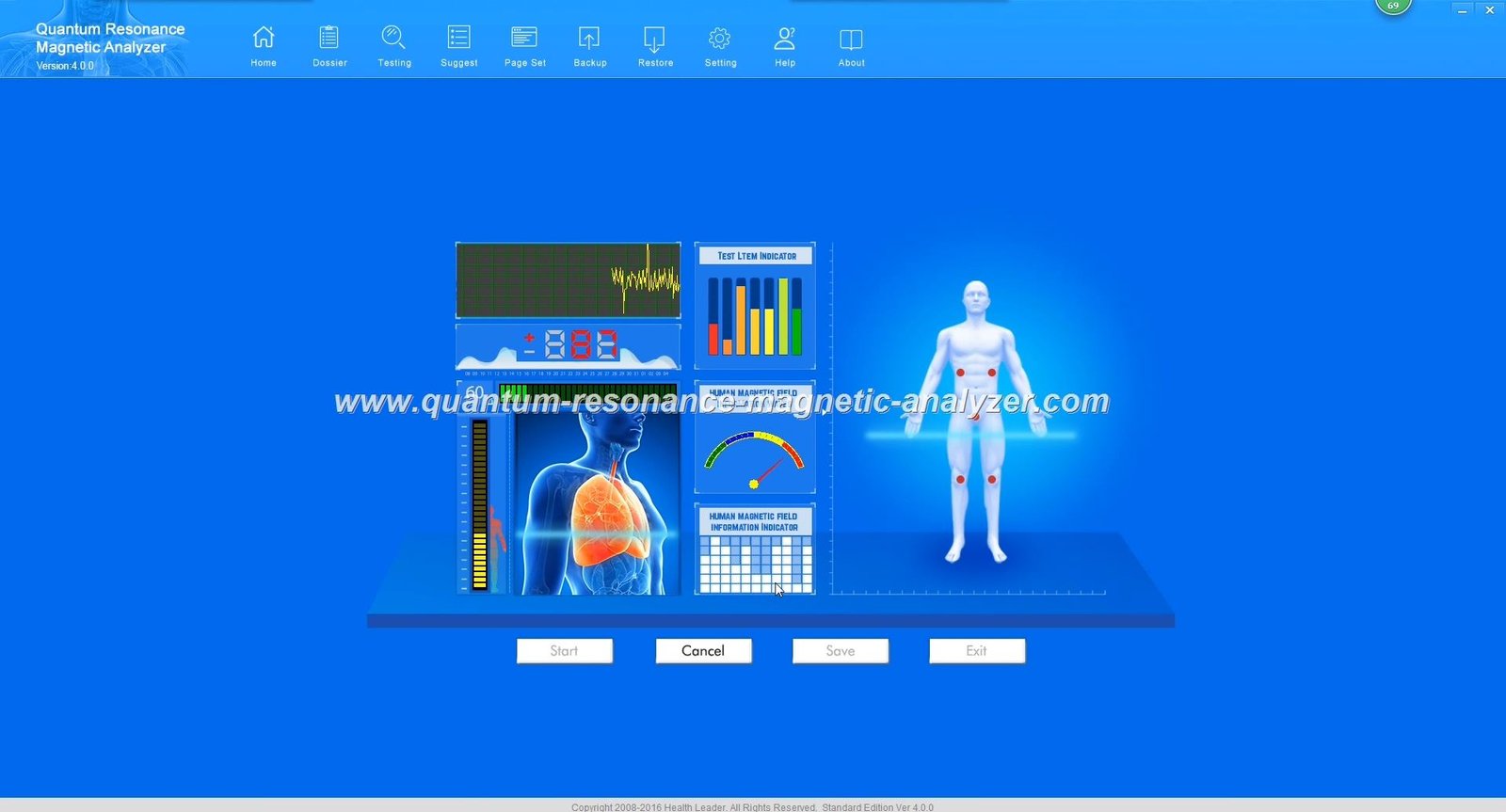
Nigeria Quantum Resonance Magnetic Analyzer
Quantum Magnetic Analyzer Machine: Advanced Technology for Comprehensive Analysis
CATEGORY AND TAGS:quantum analyzer machine enquiry
- Specifications
What is a Quantum Magnetic Analyzer Machine?
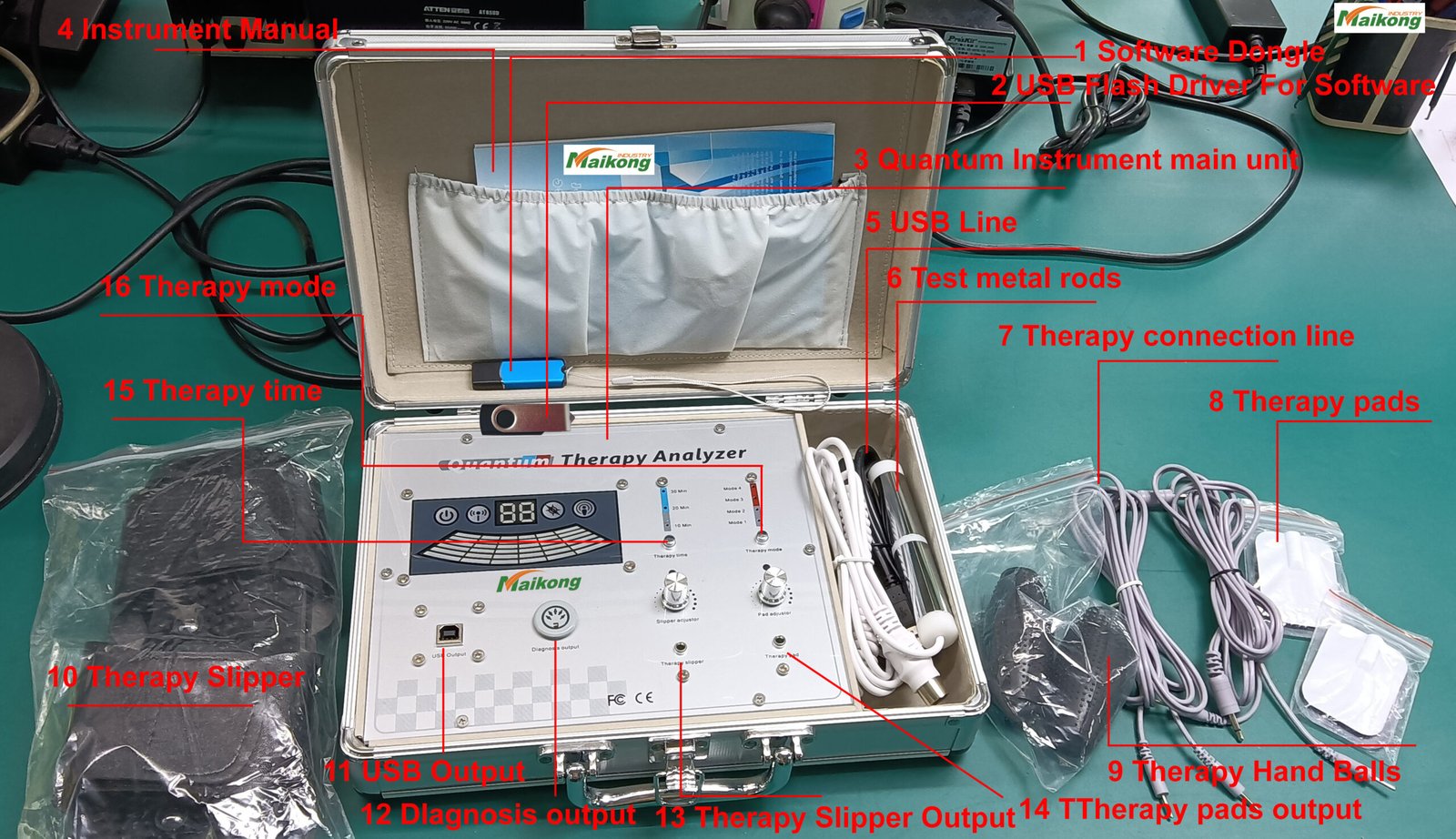

A quantum magnetic analyzer machine is an advanced diagnostic device that utilizes quantum resonance magnetic analysis (QRMA) technology to detect electromagnetic signals from the human body or material samples. By measuring these subtle energy fields, the analyzer can identify various characteristics and anomalies without invasive procedures or chemical reagents.
The technology operates on the principle that all matter emits specific electromagnetic frequencies. The quantum magnetic analyzer detects these frequency patterns and compares them against established reference databases to identify deviations or patterns indicative of particular conditions or properties.
Basic Operating Principles
The quantum magnetic resonance technology works by creating a weak magnetic field that interacts with the hydrogen atoms in the target sample. This interaction causes the atoms to align temporarily with the magnetic field. When the field is removed, the atoms return to their original state, releasing energy that can be detected and measured by sensitive sensors in the machine.
This process generates detailed data about the molecular composition and structure of the analyzed subject, whether it’s human tissue, material samples, or industrial components. The collected data is then processed through specialized algorithms to produce comprehensive analysis reports.

Key Components of Quantum Magnetic Analyzer Machines
Understanding the core components of quantum magnetic analyzer machines helps appreciate how these sophisticated devices function. Each component plays a crucial role in the accurate collection, processing, and interpretation of quantum magnetic resonance data.
Sensor Technology
The heart of any quantum magnetic analyzer machine is its sensor array. These highly sensitive electromagnetic sensors detect minute energy variations and convert them into digital signals for processing. Modern analyzers typically employ superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) or similar advanced sensors capable of detecting extremely weak magnetic fields.

Reference Databases
Comprehensive reference databases form the foundation for accurate analysis. These databases contain thousands of standardized frequency patterns corresponding to various health conditions, material properties, or industrial parameters. The quality and extent of these reference databases significantly impact the analyzer’s diagnostic capabilities.
Analysis Algorithms
Sophisticated algorithms process the raw sensor data and compare it against reference databases. These algorithms employ advanced statistical methods, pattern recognition, and increasingly, machine learning techniques to identify correlations and anomalies in the collected data.

User Interface and Reporting Systems
Modern quantum magnetic analyzer machines feature intuitive user interfaces that allow operators to control testing parameters and view results. The reporting systems generate detailed analysis reports with visualizations that help interpret the findings effectively.
Applications of Quantum Magnetic Analyzer Machines
Quantum magnetic analyzer machines have found applications across multiple fields due to their versatility, non-invasive nature, and rapid analysis capabilities. Here are the primary application areas where this technology is making significant impacts:
Healthcare Applications
In healthcare settings, quantum magnetic analyzers are used for preliminary health assessments, monitoring chronic conditions, and complementary diagnostics. The technology can evaluate various physiological parameters including cellular health, metabolic function, and potential imbalances.
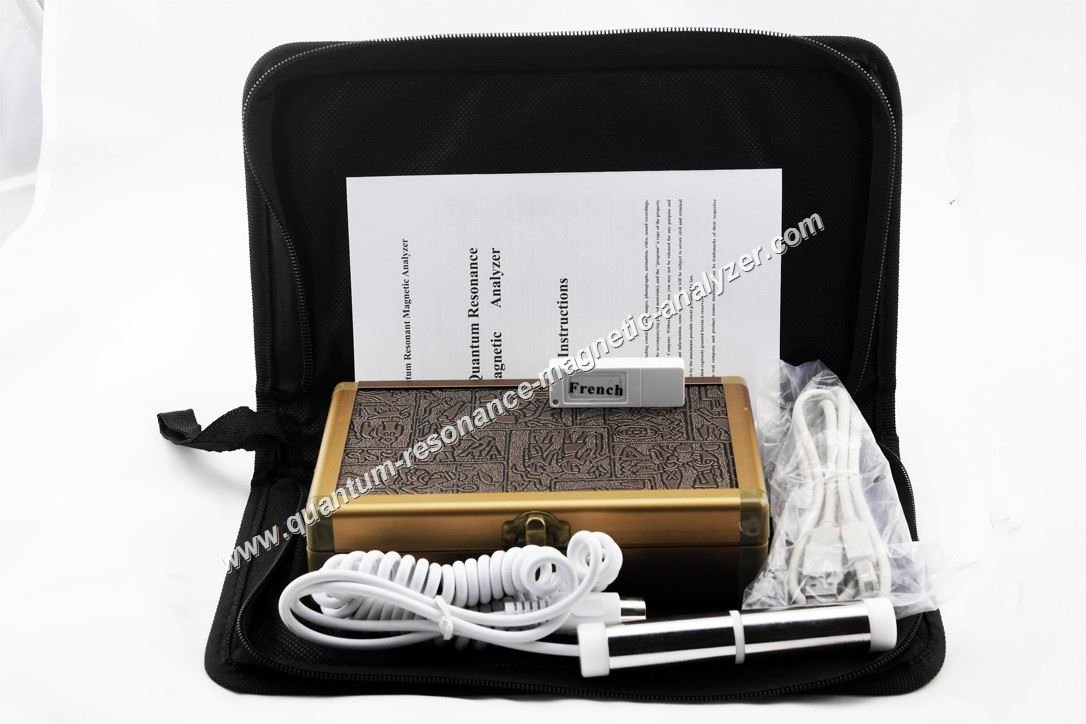

Common healthcare applications include:
- Preliminary health screenings and assessments
- Nutritional status evaluation
- Stress level monitoring
- Metabolic function analysis
- Complementary diagnostic support
Enhance Your Diagnostic Capabilities
Discover how quantum magnetic analyzer technology can complement your existing diagnostic methods with non-invasive, comprehensive assessments.
Materials Science Applications
In materials science, quantum magnetic analyzers provide valuable insights into material composition, structure, and properties without destructive testing. This capability is particularly valuable for research and quality control applications.
Key applications in materials science include:
- Non-destructive material testing
- Structural integrity assessment
- Composition analysis
- Impurity detection
- Research and development of new materials
Industrial Diagnostics
Industrial applications leverage quantum magnetic analysis for quality control, equipment monitoring, and production optimization. The technology helps identify potential issues before they cause failures or quality problems.

Industrial applications include:
- Quality control in manufacturing processes
- Equipment condition monitoring
- Failure prediction and prevention
- Process optimization
- Safety compliance verification
Quantum Magnetic Analysis vs. Traditional Methods
When compared to conventional analysis methods, quantum magnetic analyzer machines offer several distinct advantages while also having certain limitations. Understanding these differences helps determine the most appropriate applications for this technology.
| Parameter | Quantum Magnetic Analysis | Traditional Analysis Methods |
| Analysis Speed | Rapid (1-3 minutes per complete scan) | Variable (hours to days depending on method) |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Often invasive (requires samples) |
| Comprehensiveness | Multiple parameters in single scan | Usually focused on specific parameters |
| Cost Per Test | Low after initial equipment investment | Variable, often higher due to consumables |
| Operator Expertise Required | Moderate | Often high |
| Clinical Acceptance | Emerging/complementary | Well-established |
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison

Advantages of Quantum Magnetic Analysis
- Non-invasive methodology
- Rapid results (typically 1-3 minutes)
- Comprehensive multi-parameter analysis
- Minimal operating costs after initial investment
- Portable options available for field use
- No consumables or reagents required
Limitations of Quantum Magnetic Analysis
- Requires validation against established methods
- Varying regulatory acceptance across regions
- Initial equipment cost can be significant
- Database quality impacts accuracy
- Not suitable for all types of analysis
- Requires proper calibration and maintenance
Compare Analysis Methods for Your Application
Evaluate how quantum magnetic analysis compares to your current methods with our interactive comparison tool.
Case Studies: Real-World Implementations
Examining real-world implementations provides valuable insights into the practical applications and benefits of quantum magnetic analyzer machines across different sectors.
Case Study 1: Preventive Health Screening Program

Organization: Regional Wellness Center Network
Challenge: Implement cost-effective preventive health screening for a large population.
Solution: Deployed quantum magnetic analyzer machines across 12 wellness centers for rapid health assessments.
Results:
- Screened over 15,000 individuals in the first year
- Reduced screening time by 68% compared to traditional methods
- Identified early warning signs in 23% of participants
- Achieved 91% patient satisfaction rating
- Reduced overall screening program costs by 42%
Case Study 2: Advanced Materials Research Laboratory

Organization: National Materials Science Institute
Challenge: Accelerate research on novel composite materials without destructive testing.
Solution: Implemented high-precision quantum magnetic analyzers for non-destructive material characterization.
Results:
- Reduced material testing cycle by 78%
- Preserved valuable research samples for multiple tests
- Identified previously undetected structural anomalies
- Accelerated research publication output by 35%
- Enabled real-time adjustments to material formulations
Case Study 3: Manufacturing Quality Control

Organization: Precision Electronics Manufacturer
Challenge: Reduce defect rates in high-precision electronic components.
Solution: Integrated quantum magnetic analyzers into the production line for 100% component inspection.
Results:
- Reduced defect rate from 2.3% to 0.4%
- Eliminated destructive testing requirements
- Identified supplier material inconsistencies
- Achieved ROI within 9 months of implementation
- Reduced customer returns by 67%
Explore Implementation Possibilities
Discover how quantum magnetic analyzer technology can be implemented in your specific application area.
Current Limitations and Ethical Considerations
While quantum magnetic analyzer machines offer significant benefits, it’s important to understand their limitations and the ethical considerations surrounding their use.
Technical Limitations

Current quantum magnetic analyzer technology faces several technical challenges:
- Sensitivity to environmental electromagnetic interference
- Calibration requirements for consistent results
- Database limitations for certain specialized applications
- Varying results based on operator expertise
- Integration challenges with existing systems
Regulatory and Validation Challenges
The regulatory landscape for quantum magnetic analyzer machines varies significantly across regions, with different levels of acceptance and validation requirements:
- Varying regulatory classifications across countries
- Ongoing validation studies required for clinical applications
- Standards development still in progress
- Need for more extensive peer-reviewed research
Ethical Considerations

The use of quantum magnetic analyzer technology raises several ethical considerations that should be addressed:
- Ensuring appropriate use within validated applications
- Clear communication about capabilities and limitations
- Data privacy and security for analysis results
- Avoiding overreliance on technology without clinical correlation
- Equitable access to the technology across different populations
Important Note: Quantum magnetic analyzer machines should be used as complementary tools alongside established diagnostic methods, particularly in healthcare applications. Results should be interpreted by qualified professionals within the context of comprehensive assessment protocols.
Future Developments in Quantum Magnetic Analysis
The field of quantum magnetic analysis continues to evolve rapidly, with several promising developments on the horizon that will expand capabilities and applications.

Technological Advancements
Several technological innovations are expected to enhance quantum magnetic analyzer capabilities:
- Higher sensitivity quantum sensors for more precise measurements
- AI and machine learning integration for improved pattern recognition
- Miniaturization enabling more portable and accessible devices
- Enhanced reference databases with more comprehensive parameters
- Cloud-based analysis capabilities for distributed diagnostics
Emerging Applications
New application areas are emerging as the technology matures:
- Environmental monitoring and pollution detection
- Food safety and quality assessment
- Personalized medicine and treatment response monitoring
- Advanced materials development and testing
- Integration with IoT systems for continuous monitoring
“The integration of quantum sensing technologies with artificial intelligence represents the next frontier in non-invasive analysis methods, potentially revolutionizing how we approach diagnostics across multiple industries.”
Frequently Asked Questions
Are quantum magnetic analyzer machines safe to use?
Yes, quantum magnetic analyzer machines are generally considered safe. They use weak magnetic fields similar to those encountered in everyday environments. The technology is non-invasive and does not emit harmful radiation. However, as with any electronic device, they should be used according to manufacturer guidelines and may have specific contraindications for certain individuals, such as those with pacemakers or other implanted electronic devices.
What is the typical cost range for quantum magnetic analyzer machines?
The cost of quantum magnetic analyzer machines varies significantly based on capabilities, precision, and intended applications. Entry-level systems typically range from ,000 to ,000, while advanced professional systems with comprehensive databases and enhanced features can range from ,000 to ,000 or more. Additionally, some manufacturers offer subscription models for database updates and software enhancements.
How accurate are quantum magnetic analyzer results?
Accuracy varies depending on the specific device, application, and reference databases used. In well-established applications with proper calibration, studies have shown correlation rates of 75-85% with conventional testing methods. However, accuracy can be influenced by environmental factors, operator expertise, and the quality of reference databases. For critical applications, results should be validated with established methods.
What maintenance is required for quantum magnetic analyzer machines?
Maintenance requirements typically include regular calibration (usually quarterly or bi-annually), software updates, sensor cleaning, and occasional professional servicing. Most manufacturers recommend annual technical inspections to ensure optimal performance. Proper environmental conditions (stable temperature, humidity, and minimal electromagnetic interference) are also important for consistent operation.
Can quantum magnetic analyzers replace traditional diagnostic methods?
Quantum magnetic analyzers are generally considered complementary rather than replacement technologies. While they offer advantages in speed, non-invasiveness, and comprehensive screening, they are most effective when used alongside traditional methods, especially for critical diagnostic decisions. Their strength lies in rapid screening, monitoring trends, and identifying areas for more focused investigation.
Conclusion
Quantum magnetic analyzer machines represent a significant advancement in non-invasive analysis technology with applications spanning healthcare, materials science, and industrial diagnostics. Their ability to provide rapid, comprehensive assessments without invasive procedures or chemical reagents offers compelling advantages in many scenarios.
While the technology continues to evolve and address current limitations, its value as a complementary tool alongside established methods is increasingly recognized. Organizations implementing this technology report benefits in efficiency, cost reduction, and expanded capabilities.
As research advances and regulatory frameworks mature, we can expect quantum magnetic analysis to play an increasingly important role in various fields, particularly as integration with AI and machine learning enhances its analytical capabilities.
Experience Quantum Magnetic Analysis Technology
Ready to explore how quantum magnetic analyzer technology can benefit your organization? Schedule a personalized demonstration with our technical specialists.

Contact us By WhatsApp: